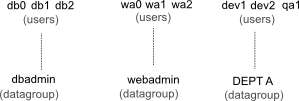Datagroups define user access to data. A simple set up would assign a user to datagroup that represents an organisational unit such as a team or application area.
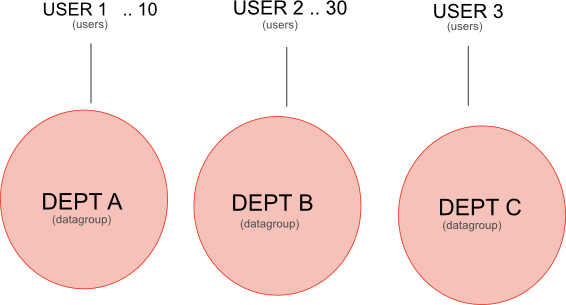
Each datagroup is made up of a list of data sources. A datagroup can also contain a list of data sources to exclude from its definition.
Dept A include: tag: www,db,proxy,dbbus
Dept B include: tag: mongodb,cache-store,
Datagroups can represent hiereachical relationships through nesting other data groups. The ability to combine datagroups to form new datagroups provides a versatile and flexible means of expressing data access rules.
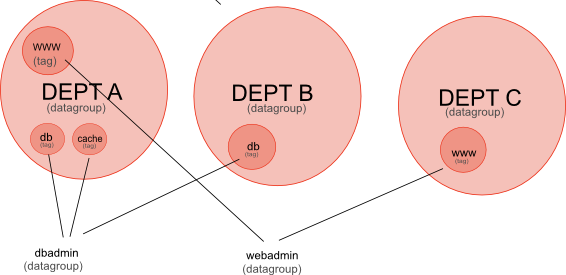
The diagram above shows data siloed into different departments, subsets of data representing different applications and the data access roles that limit access to different application across departements. Translating the diagram into a tree gives a clearer view of the relationships involved.

This can be represented in Logscape using the following data rules.
Datagroup: dbadmin
children: DeptA,DeptB
include: db,cache
Datagroup: webadminSetting up the Users
children: DeptA,DeptC
include: www
Once the datagroups have been created the users can be set up. Each user is mapped onto a datagroup that represents their data acceess. A user can be mapped onto any part of the datagroup hierarchy and will only have access to the data represented by it.